News & press releases
Smart city use case, towards a urban-scale air quality model
LEGaTO use cases focus on improving the energy efficiency of the computational solutions for increasingly important societal challenges. The smart cities use case addresses air pollution data collected from sensors.
Air quality and associated impacts on public health are matters of growing concern in many urban areas. The emission and dispersion of critical pollutants (PMx, O2 and ground-level O3) correlate with cancer, asthma, cardiorespiratory problems, brain development in children and reduction of life expectancy in general. Consequently, air quality monitoring networks and modelling forecasting systems are critical to increase awareness and, ultimately, to assist decision-makers on the adoption of measures to protect public health.
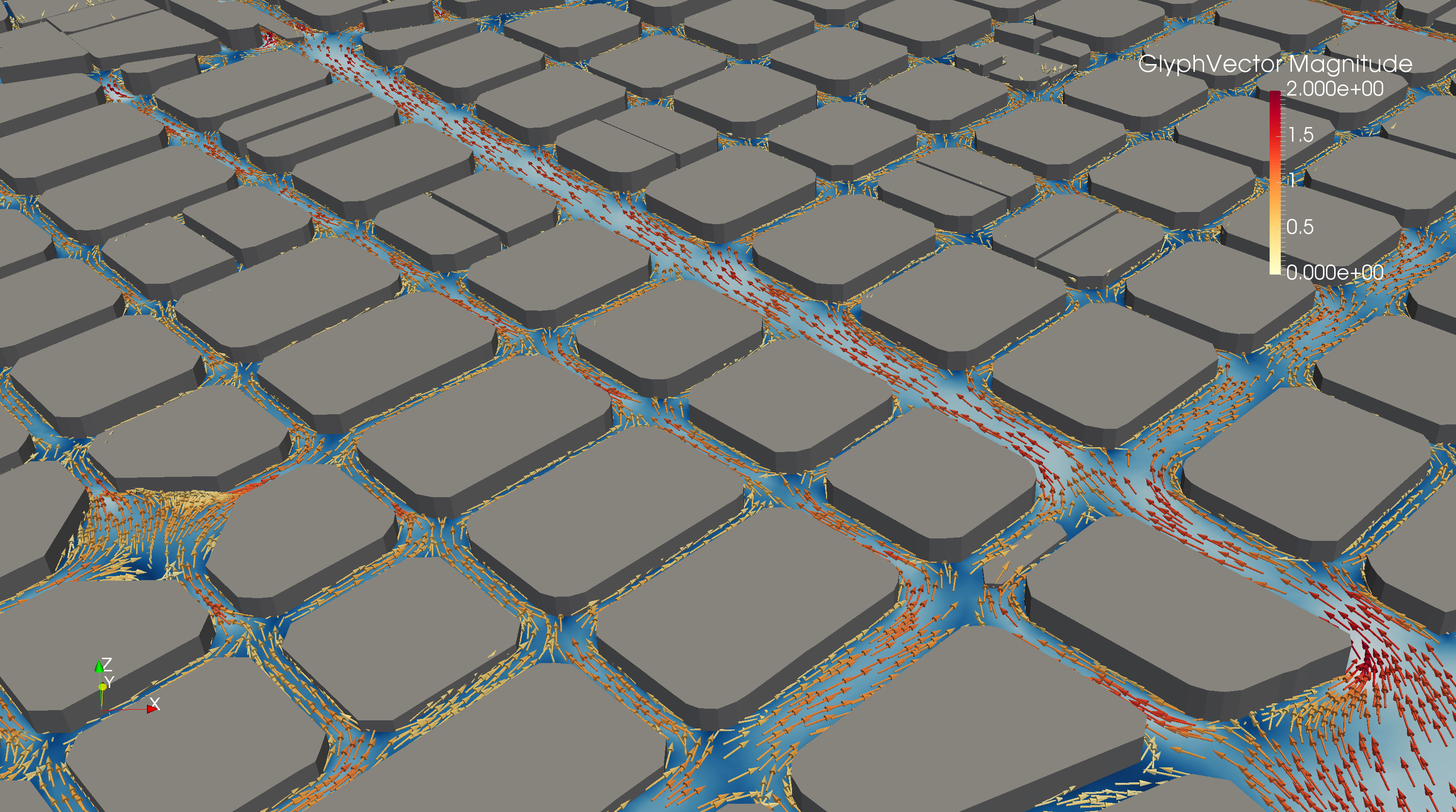
Predicting models that combine large datasets and high-fidelity numerical simulations are utilized for predicting the propagation of liquid and atmospheric pollutants in urban environments. The simulations are based in CFD techniques that have large computing demands, requiring optimizations in performance and energy efficiency. First, the wind flow through the urban section is simulated considering different wind directions. The development of the flow is saved, and the simulation is restarted combining the database information to predict the transport of pollutant substances.
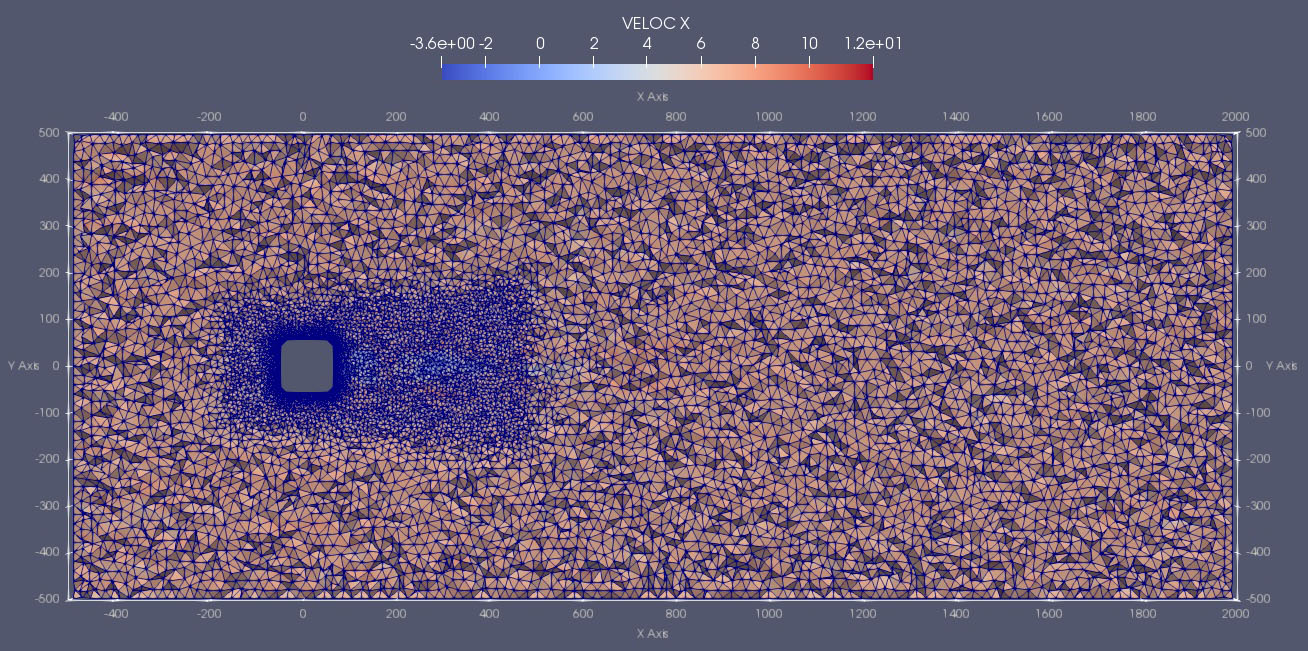
In this scenario, the LEGaTO stack is pivotal, in terms of both leveraging processing capabilities and improving the energy-efficiency of an operational urban-scale air quality modelling system. The Smart City use case aims at demonstrating that monitoring of urban air quality through CFD simulations is feasible for nowcasting predictions in an operational workflow. A case consisting of 12 city blocks of the Eixample neighbourhood in Barcelona was selected as a benchmark.